A Safer Tomorrow: AESOP Technology's Battle Against Look-Alike, Sound-Alike Medication Errors10/24/2023
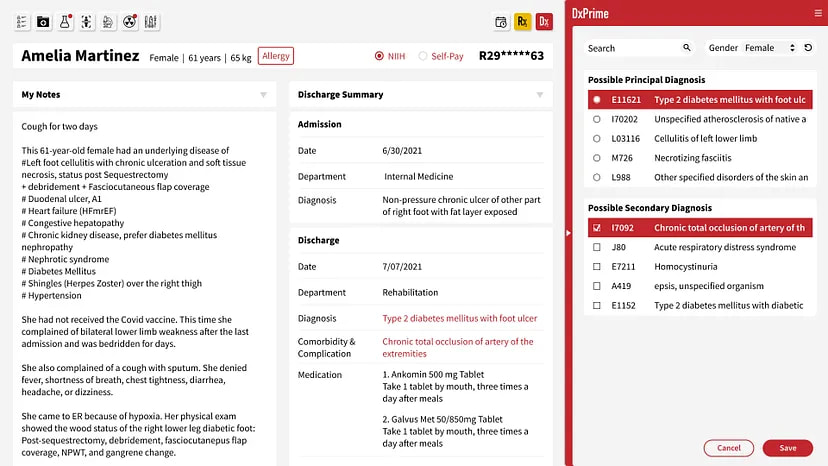
Medication errors are a critical problem in healthcare, and Look-Alike, Sound-Alike (LASA) medication errors pose a particularly daunting challenge. Studies show that LASA errors account for approximately one in four medication errors, making them a significant threat to patients. AESOP Technology is thus pleased to announce remarkable results from its recent clinical research, demonstrating its exceptional effectiveness in preventing LASA errors. "Accurately identifying LASA errors can be challenging due to their complex origins. Surprisingly, only about 15% of intercepted wrong drug errors during our study could be clearly categorized as LASA errors, in the sense that the medications had similar names that contributed to the mix-up. The LASA errors also did not follow predictable patterns, with only 9 out of 71 cases repeating. These findings underscore the limitations of conventional human-defined rule systems, even when augmented with reinforcement learning. RxPrime (formerly MedGuard) not only detects errors that were not previously identified but also highlights the essential need for AI with advanced medical knowledge, demonstrating a breakthrough in patient safety in healthcare," said Jim Long, CEO of AESOP Technology, explaining the intricacies of detecting medication errors, specifically LASA errors. AESOP also leverages its proprietary AI technology to overcome the limitations of traditional clinical decision support systems and address the issue of alert fatigue. "AESOP has taken additional steps to improve problem list documentation to reduce alert fatigue from LASA error detection. Many alerts contributing to physician fatigue result from poor problem list documentation within electronic health record systems. Thus, AESOP intervened at the source by helping physicians complete clinical diagnoses and documentation more effectively while prescribing," Long added. More than half of all medication errors occur during the prescription phase, making it a critical focus for improving patient safety. AESOP's innovative approach offers a beacon of hope. Applying advanced AI technology to this complex problem has yielded impressive results and holds great promise for the healthcare industry. As we address patient safety challenges, AESOP Technology's contributions stand as a testament to the potential of innovative solutions in ensuring the well-being of patients worldwide. Reference: yahoo finance
SOAP Health's conversational AI for medical encounters, risk and symptom assessment, and documentation integrates with AESOP Technology's electronic medical record data analysis for clinical decision optimization, coding, and productivity.
SOAP Health and AESOP Technology are excited to announce a transformative partnership that will push the boundaries of AI-enhanced medical encounters. This collaboration combines AESOP's cutting-edge DxPrime and DeepDRG solutions with SOAP Health's patented and clinically validated Ideal Medical AI Assistant™ to fuse patient-reported data with Electronic Medical Record Systems (EMRs) data to create Precision Patient Profiles™ that give physicians the most comprehensive view and understanding of their patients to improve speed to diagnosis, workflow efficiency, and revenue. Steven Charlap, MD, MBA, CEO of SOAP Health, believes this alliance marks a milestone in effectively integrating AI into clinical encounters. "By incorporating AESOP's DxPrime into our existing solutions, we are elevating the realm of data-driven clinical decision-making. DxPrime's DeepDRG and Natural Language Processing capabilities are revolutionary, enhancing the quality and efficiency of data analysis and diagnostic decisions," said Dr. Charlap. "Combined with SOAP's patented and clinically validated Ideal Medical AI Assistant™, this partnership promises to enhance medical encounters, providing a robust, integrated solution that is unparalleled in today's market." Combined with SOAP's integration with Dolbey Fusion Narrate™, a previously announced partnership, the Precision Patient Profile™ will seamlessly integrate into over 100 EMRs, fortifying the power of these applications to deliver value to physicians. "The joint venture between AESOP Technology and SOAP Health promises to radically optimize physician data collection and medical coding," says Jeremiah Scholl, Co-founder and CPO of AESOP Technology. "Our shared mission is to harness the power of AI to improve patient outcomes and clinical efficiency, and this partnership is a giant leap toward fulfilling that commitment." SOAP Health's vision to reduce diagnostic errors aligns perfectly with AESOP's focus on improving the quality and efficiency of clinical decision-support and medical coding. This partnership is poised to bring significant advancements in physician practice, optimizing patient care and safety. For more details on how SOAP Health and AESOP Technology are collaborating, please visit the SOAP Health Partner Page at www.soap.health/aesop About AESOP Technology AESOP Technology harnesses advanced AI to improve the clinical decision-making process, enhance medical coding quality, and prioritize patient safety. AESOP's flagship products, DxPrime and DxCode, boast 99% accuracy in identifying and analyzing data and integrate directly into physicians' clinical workflows. DeepDRG is the unique AI approach they developed to unlock understanding of how diagnoses are typically associated with structured clinical data like lab results, medications, and procedures. To learn more about AESOP Technology, visit aesoptek.com. About SOAP Health SOAP Health is a trailblazer in medical practice AI. Through patented conversational and generative AI, SOAP's mission is to save lives by reducing diagnostic errors, accounting for over 800,000 preventable deaths and permanent disabilities each year. The company leverages the collective expertise of seasoned medical entrepreneurs, scientists, and technologists to deliver clinically validated solutions. To learn more about SOAP Health, visit soap.health.
Referred: BENZINGA
從健保資料庫挖礦 終成臨床編碼唯一服務供應商
「我們始終想要用數據來做應用。」醫守科技執行長暨聯合創辦人龍安靖笑說,雖然曾被說不學無術,但團隊仍默默投入健保資料庫資料研究分析,靠著一股堅持,將數以百計的光碟片,一一讀取。也因為進得夠早、走得夠久、探得夠深,讓醫守得以成為臨床編碼唯一服務供應商,與臺灣的簽約數呈倍數成長,在數位發展部數位產業署的「資料經濟價值躍升計畫」支持下,也於美國傳來好消息,未來全球市場精彩可期。 由世界衛生組織建立的疾病分類系統,目的是把跨國家、地區在一定期間所蒐集的罹病或死亡資料,能夠系統化記錄、分析、解讀與比較,現已成為病歷書寫的重要部分。住院過程中,一位病患的病歷,作者群是經手過該病患治療歷程的所有醫師,他們會記錄病患主觀陳述、客觀檢查結果、曾經進行的手術或處置,最後進行病歷總結,再交給疾病分類人員分別進行疾病分類編碼,用以進行健保給付申報。 全球健保制度經過數十年的演進,申報制度大量引進各種編碼系統,為了整合各個複雜的系統,醫院需要耗費大量人力、物力,付出許多額外成本,更造成醫院的損失。臺灣健保疾病分類於2016年起以ICD-10 CM/PCS(International Statistical Classification of Disease and Related Health Problems, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification / Procedure Coding System,國際疾病分類第十版)申報後,編碼數量大幅增加,也提高了臨床編碼的困難度。尤其,當醫師面對較不熟悉的處置碼和非本身專業科別的疾病,要選擇最正確且合適的編碼,相當挑戰與費時,導致疾病分類師必須花費更多的心力調整和修正醫師所選的編碼,更遑論進行在院編碼和品質稽核。 AESOP Technology, in collaboration with AstraZeneca Taiwan, has unveiled Medigator, an innovative AI software designed to manage immune-related adverse events (irAEs) and enhance the effectiveness of immunotherapy. With cancer being the second leading cause of death and immunotherapy offering improved survival rates, Medigator is specially designed to address the potential challenges associated with irAEs that may deter some patients from choosing this treatment. The American Cancer Society estimates that of the 2 million new cancer cases in the U.S. in 2023, about half could be eligible for immunotherapy treatment. While this treatment stimulates the patient's immune system to fight cancer, it can potentially trigger an overactive immune response, leading to irAEs. Managing irAEs is challenging due to the unique immune responses and variability in the reaction to immunotherapy. The intensified immune response that fights cancer cells can inadvertently harm normal tissues. Effective communication is crucial to educate patients about possible side effects, readiness for assistance, and timely medical intervention. Mild irAEs can often be managed symptomatically with topical treatments, while severe cases may require discontinuing immunotherapy and administering immune-suppressing medications. To address the complexities of managing irAEs, Medigator offers real-time assistance to physicians. This tool manages the risk of irAEs and is seamlessly integrated into the Computerized Physician Order Entry system. "By harnessing the power of big data analytics, Medigator analyzes real-world patient experiences with irAEs, physicians' management strategies, and patient responses to treatment based on a dataset of 197,921 claim-based prescriptions. Using these analytical parameters, Medigator goes a step further by predicting the risk levels of different irAEs in individual patients. It provides personalized medication options by considering factors such as patient age, gender, race, chronic medical conditions, and genetic history, empowering physicians to enhance their risk management strategies in the care plan," explained Jim Long, CEO of AESOP Technology. "Medigator is an immunotherapy medication navigator designed for physicians. It aims to minimize interruptions in immunotherapy, preserve valuable treatment time and resources, and alleviate the treatment burden," said Jim Long. "The origin of the partnership between AESOP Technology and AstraZeneca Taiwan traces back to 2019 at an international biomedical accelerator co-hosted by AstraZeneca A.Catalyst Network and the National Biotechnology Research Park in Taiwan, which is dedicated to exploring new possibilities to change patients' lives. Medigator has set a promising example demonstrating patient-centric innovation by advancing shared decision-making in precision medicine," said Ben Chen, Medical Director, AstraZeneca Taiwan. The research findings of Medigator, which were recently presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, received notable attention. AESOP Technology continues its unwavering commitment to delivering physicians with precise and personalized solutions for irAEs as immunotherapy advances. Its ultimate goal is to enhance immunotherapy treatment outcomes and improve patients' overall quality of life. 
李宛庭
「solaxin」與「solian」兩個極其相似的藥名,實際卻是天差地遠的藥品,分別是肌肉鬆弛劑和抗精神病藥。另外,每家藥廠又都有著各自的命名方式,因此即使是聰明又小心的醫生,也可能不小心開錯藥。 開錯藥品可能帶來的風險,不只是患者無法得到妥善的治療,還有可能導致誤食過敏藥物、產生其他副作用等嚴重後果。 2019年,醫守科技看見了醫療產業開錯藥的問題,開發RxPrime藥御守協助解決,現今則推出DxPrime好完診進軍診斷系統服務,今(2022)年8月更完成了295萬美元(約新台幣8,850萬元)的Pre-A輪募資,由台杉資本領投、日本知名上市遊戲公司Colopl Next、美國創投500 Global和比翼生醫創投等跟投。 從原先的「藥物開立服務」跨足「診斷系統服務」,醫守科技究竟看見了哪些產業問題? 從「用藥」到「診斷」,醫守科技如何從知名產品RxPrime藥御守轉型再出發? 2019年成立的醫守科技,最先推出的產品是RxPrime藥御守,希望為醫生減少開錯藥的狀況。藥廠出廠藥品時,會為藥品命名,相似的藥名卻可能是天差地遠的藥品,於是醫守科技的RxPrime藥御守,透過機率模型與增強學習雙重人工智慧引擎,打造用藥安全演算法,在偵測到藥品可能開錯時,即時發出系統警告提醒醫生。 儘管推出RxPrime藥御守立意良好,醫守科技卻面臨到了醫院採購的系統性問題。
Digital health startup AESOP Technology has raised a $2.95 million series pre-A round to address the growing medical and billing errors problem. The round was led by Taiwania Capital with participation from Colopl Next, 500 Startups, and BE Capital.
Originally from Taiwan, AESOP started as a university spin-off from Taipei Medical University (TMU). Professor Yu Chuan (Jack) Li, the founder and current president of the International Medical Informatics Association, spent ten years before AESOP working on big data approaches to reduce medication errors. He initially applied the model to launch a product, RxPrime (previously known as MedGuard), that identifies wrong-drug errors. During the pandemic in 2020, Prof. Li officially established AESOP in the US with his former student, who grew to become CIO of a TMU-affiliated hospital, Dr. Jim Long, and former TMU Visiting Assistant Professor, Dr. Jeremiah Scholl. They worked together to broaden the types of errors the AI could identify and on products they could use to improve the US healthcare system. "Our solution is revolutionary and generalizable." CEO Jim Long described. "We have developed an AI model with an exceptional understanding of the association between diagnoses and structured clinical data like medications, lab results, and procedures." One of the first errors RxPrime identified was a 9-year-old girl accidentally prescribed an anti-schizophrenia drug for simple back pain. Another commonly prescribed error was Acetaminophen (pain killer), sometimes mistaken as Acetazolamide (glaucoma and altitude illness). "These mistakes might occur just because the two drugs have look-alike or sound-alike (LASA) names. It is horrible to think about, but errors like LASA happen in hospitals everywhere." Jim explained
AESOP Technology announced that they have been accepted into Mayo Clinic Platform_Accelerate, a 20-week program that helps early-stage health tech AI startups get market-ready.
Participants are selected through a competitive screening process where a panel of Mayo Clinic leaders reviews them from the clinical and operational perspective, led by John Halamka, MD., President of Mayo Clinic Platform. "It's an excellent opportunity for a medical AI startup like us. Data is the fuel from which everything grows into power, and this program provides de-identified patient datasets and tools to help us validate our solutions," says Jeremiah Scholl, the CPO of AESOP Technology. "This practical experience will help us go even further in developing better products. The fact that we get to be mentored by Mayo Clinic's reputable experts is inspiring." 'AESOP', which stands for 'AI-Enhanced Safety of Prescription', is working to make physician data entry easier, faster, and less error-prone using machine learning on 3.2 billion data sets. The company has developed products capable of this. One is RxPrime which detects wrong drug errors by checking if medications match patients' diagnoses, age, and gender. Errors can happen at any stage of the medication-use process, but more than 50% of them occur during the prescribing phase. RxPrime is able to detect potential and unexplained errors in prescriptions and provide optimal recommendations, even for the look-alike-sound-alike medication errors. It offers just-in-time decision support without interfering unnecessarily with the clinical consultation process. |
全部
|
醫守科技股份有限公司
|

|
© AESOP Technology 2024